
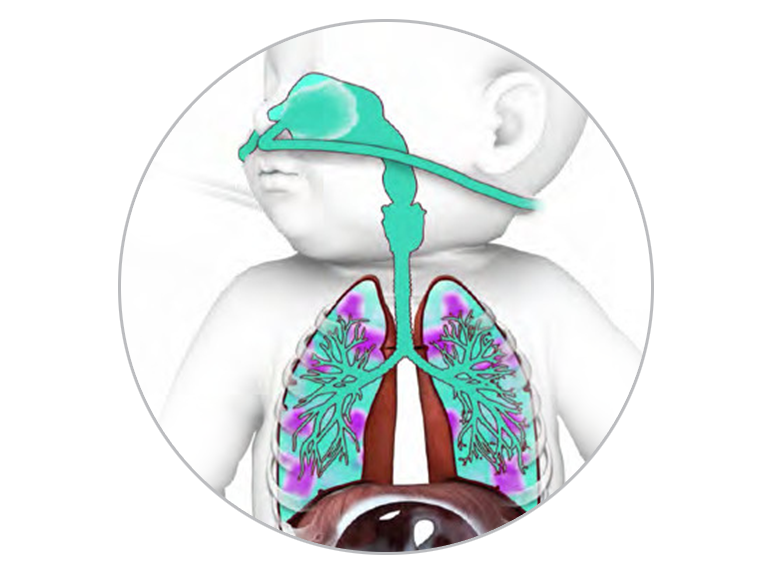

Keeping this in view, what does adding mechanical dead space do? Physiological dead space ( total dead space ) is the portion of a tidal volume that does not participate in gas exchange because it either remains in the conducting airways (anatomic dead space) or does not get in contact with blood flowing through the pulmonary capillaries (alveolar dead space). Recall that the conducting airway (anatomical dead space) has a volume of ~150 ml. (the bohr equation is used to justify the inclusion of half the second phase in this calculation.) click to see full answer. Volume of the conducting airways, approximately 150 ml. In figure 1, the difference between physiologic dead space (ok ) and anatomical dead space (ob ) is bk, which therefore represents alveolar dead space, vd alv. Dead space represents the volume of ventilated air that does not participate in gas exchange.

Closing volume is the volume towards the end of a forced expiration, after which some airways have effectively closed and more of the expired gas comes more from the. How To Calculate Anatomical Dead Space - Understanding the equation will simplify the concept of dead space greatly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
